scipy.signal.nuttall¶
-
scipy.signal.nuttall(M, sym=True)[source]¶ Return a minimum 4-term Blackman-Harris window according to Nuttall.
This variation is called “Nuttall4c” by Heinzel. [R256]
Parameters: M : int
Number of points in the output window. If zero or less, an empty array is returned.
sym : bool, optional
When True (default), generates a symmetric window, for use in filter design. When False, generates a periodic window, for use in spectral analysis.
Returns: w : ndarray
The window, with the maximum value normalized to 1 (though the value 1 does not appear if M is even and sym is True).
References
[R255] A. Nuttall, “Some windows with very good sidelobe behavior,” IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 84-91, Feb 1981. DOI:10.1109/TASSP.1981.1163506. [R256] (1, 2) Heinzel G. et al., “Spectrum and spectral density estimation by the Discrete Fourier transform (DFT), including a comprehensive list of window functions and some new flat-top windows”, February 15, 2002 https://holometer.fnal.gov/GH_FFT.pdf Examples
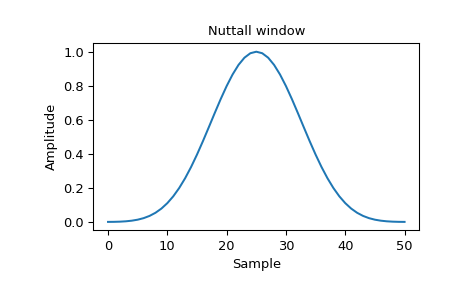
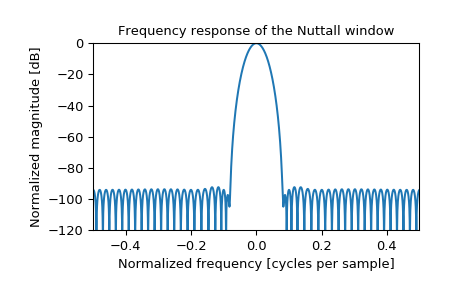
Plot the window and its frequency response:
>>> from scipy import signal >>> from scipy.fftpack import fft, fftshift >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> window = signal.nuttall(51) >>> plt.plot(window) >>> plt.title("Nuttall window") >>> plt.ylabel("Amplitude") >>> plt.xlabel("Sample")
>>> plt.figure() >>> A = fft(window, 2048) / (len(window)/2.0) >>> freq = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, len(A)) >>> response = 20 * np.log10(np.abs(fftshift(A / abs(A).max()))) >>> plt.plot(freq, response) >>> plt.axis([-0.5, 0.5, -120, 0]) >>> plt.title("Frequency response of the Nuttall window") >>> plt.ylabel("Normalized magnitude [dB]") >>> plt.xlabel("Normalized frequency [cycles per sample]")